Tiny Dense Forests are Springing up Around Europe
The Guardian, June 2020 - Fanny Agostini, édité par Maxime Dewilder 17h35, le 18 novembre 2019, modifié à 17h35, le 18 novembre 2019
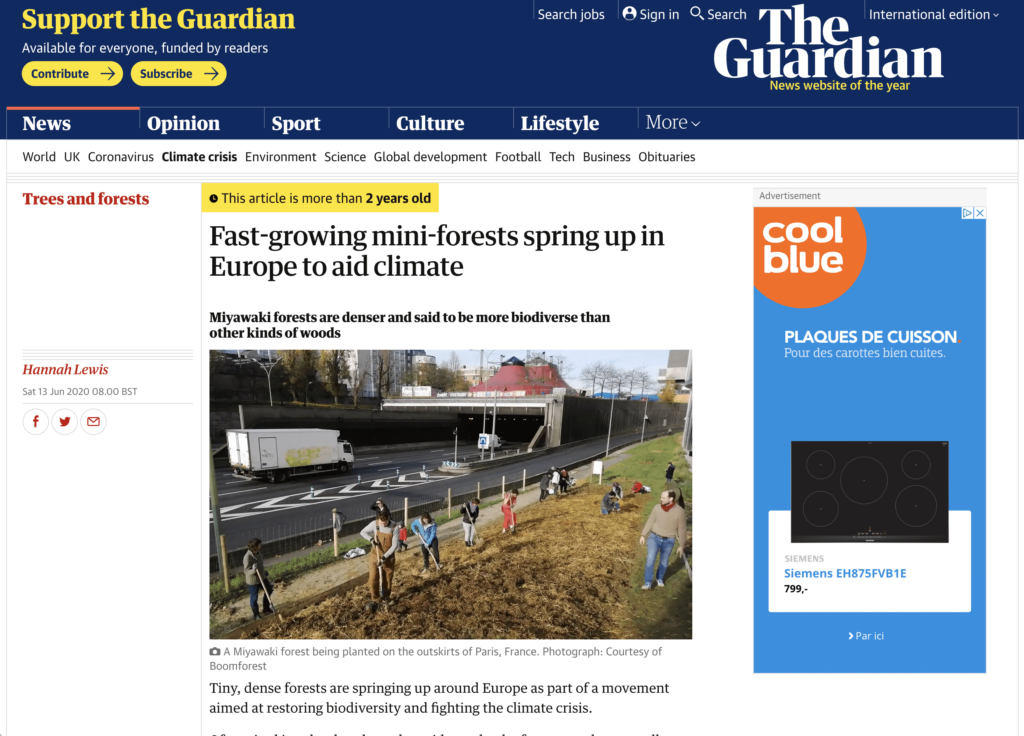
Fast-growing mini-forests spring up in Europe to aid climate
Tiny, dense forests are springing up around Europe as part of a movement aimed at restoring biodiversity and fighting the climate crisis.
Often sited in schoolyards or alongside roads, the forests can be as small as a tennis court. They are based on the work of the Japanese botanist Akira Miyawaki, who has planted more than 1,000 such forests in Japan, Malaysia and elsewhere.
Advocates for the method say the miniature forests grow 10 times faster and become 30 times denser and 100 times more biodiverse than those planted by conventional methods. This result is achieved by planting saplings close together, three per square metre, using native varieties adapted to local conditions. A wide variety of species – ideally 30 or more – are planted to recreate the layers of a natural forest.
Scientists say such ecosystems are key to meeting climate goals, estimating that natural forests can store 40 times more carbon than single-species plantations. The Miyawaki forests are designed to regenerate land in far less time than the 70-plus years it takes a forest to recover on its own. [...]